In the early years of growing without daylight, most of the attention was on the development of leafy crops like lettuce, herbs, and microgreens. These crops have a fast turnaround time, high harvest efficiency, and require relatively little labor to grow, so it is easier to automate their cultivation. In recent years, there has been more and more interest in soft fruits, such as strawberries, and a great deal of attention has been paid to dwarf varieties of, for example, tomatoes and sweet peppers. But what other possibilities are there for indoor farming? And how can this technology be applied to improve the crops in greenhouses or fields?

A strong start for fast and uniform growth in lettuce
One of the most important growth phases for plants is their start: the raising from seed to young plant material. This crucial foundation can make or break a crop, with consequences for both growers and retailers, as well as food processors. Increasingly Signify are seeing the impact of changing weather conditions on the availability of products on supermarket shelves. More control over the plant raising phase may help reduce risks in cultivation and improve the results. Grafting tomatoes in the middle of summer has become challenging due to the high temperatures while growing lettuce plants in winter can easily take up to 60 days. When the starting phases take place in a climate-controlled environment without exposure to daylight, growers can provide an optimal product year-round without the weather impacting it.
Signify has been focusing on improving the plant raising phase at their GrowWise Research Center for several years now. In a series of trials, lettuce plants were raised in a controlled environment using LED lighting and then transplanted to a professional grower's field. The findings: they grow faster and more uniformly, and a larger number of them grow well in the field. These trials demonstrate that the plant is less affected by transplanting and takes root sooner, achieving faster exponential growth (see Figure 1) and resulting in a significantly shorter cultivation time. This could result in more crop cycles per year on the same surface area, ultimately leading to higher production per square meter.
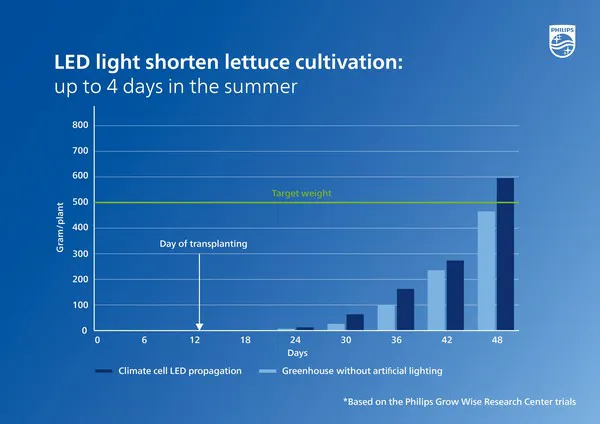 Figure 1: Growth curve of two different raising methods. "Traditional raising" refers to plants raised traditionally in a greenhouse without artificial lighting. "Indoor Farm propagation" is the curve for the young plants raised in a climate cell without daylight as a function of the time in the field after transplanting.
Figure 1: Growth curve of two different raising methods. "Traditional raising" refers to plants raised traditionally in a greenhouse without artificial lighting. "Indoor Farm propagation" is the curve for the young plants raised in a climate cell without daylight as a function of the time in the field after transplanting.
Effect of far-red light on raising cucumbers and tomatoes
It is well known that the light spectrum can have a major effect on the morphology of plants. However, the specific effects of different colors of light on the growth and development of young plants and the subsequent impact on the crop after transplanting it into a greenhouse or field are still largely unknown. In Signify's research program on the raising of heated vegetable plants, Signify is looking at various facets of these crops. For example, experiments have been carried out to improve uniformity in seedlings, success rates when grafting in climate chambers, and shoot development after pinching tomatoes.
In recent research, Signify has shown that the use of far-red light during the raising phase of cucumbers can promote the elongation of the crop, creating an open plant structure. In tomatoes, however, it can lead to uneven shoot development. The increasing levels of far-red light in the treatments cause an increasing non-uniformity in the development of the shoots in the young plants (see Figure 2). This suggests that far-red light is not necessary for raising tomatoes and can even have negative effects to some extent. This can be attributed to the physiological impact of far-red light on the hormone balance in plants, which can stimulate apical dominance and give prominence to the growth of the shoot. The combination of this knowledge and advances in the company's dynamic lighting techniques gives growers more control over the crop and the ability to provide the right light spectrum at the right time.
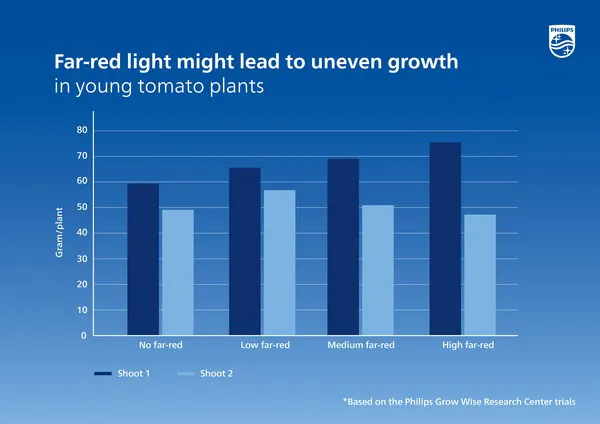 Figure 2: Difference between shoots 1 and 2 in a tomato plant with two heads under different light treatments with increasing amounts of far-red light. The weight of shoot 1 remains almost the same with the different treatments. Shoot 2 increases in weight with increasing fractions of far-red light.
Figure 2: Difference between shoots 1 and 2 in a tomato plant with two heads under different light treatments with increasing amounts of far-red light. The weight of shoot 1 remains almost the same with the different treatments. Shoot 2 increases in weight with increasing fractions of far-red light.
Three options for more control over the raising phase
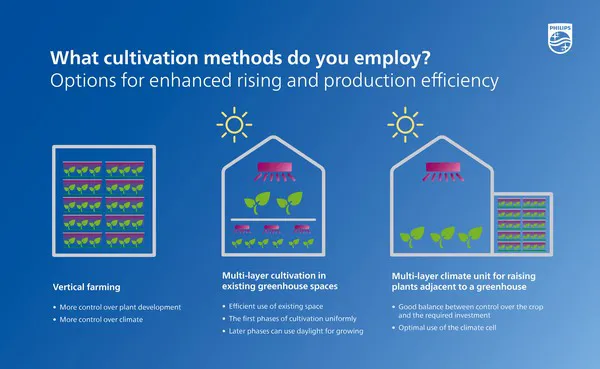
Raising young plants to increase production in greenhouses offers countless possibilities. Many growers are initially deterred from using multi-layer cultivation systems because of the futuristic look, and they often think immediately that it will mean major investments that seem to be too much to handle. Nevertheless, there are several ways to integrate this new development into current techniques and cultivation situations. The unique circumstances of each situation offer opportunities in various areas.
- For example, a "greenhouse without glass" could be a viable option in cases where enough land is available. In this type of greenhouse, the same techniques can be used as in a traditional greenhouse, isolated and with more control over climate, and therefore over plant development.
- If expansion to a larger area is not possible, multi-layer cultivation can be very profitable. This method doubles the cultivation area for each additional layer installed, allowing for more efficient use of existing greenhouse space. In addition, the first phases of cultivation can be used uniformly for germination, rooting, or raising, while later phases can use daylight for growing on or hardening off. There are already some examples of this application available in which multi-layer cultivation is being used successfully in greenhouse construction.
- A third option is to build a multi-layer climate unit for raising young plants next to an existing greenhouse. The plants can be transferred directly to the greenhouse after the raising stage. Certain crops, such as lettuce or herbs, are particularly suitable for these setups. This makes optimal use of the climate cell, in which the plants are raised at a high plant density and then, when transplanted, they are moved to a greenhouse with lower plant densities. This allows you to create a good balance between control over the crop and the required investment. This situation already has some success stories, and the "future" may be closer than we think.
Further developments
The company will have several trials taking place in their GrowWise Research Center next season in order to keep raising crops without natural light. Young plants raised without daylight will be transplanted into the greenhouse so they can monitor the growth process of the plants. Growth rate, harvest weights, dry matter production, flower development, fruit set, and many other aspects will be monitored, depending on the type of crop. In all these trials, the current standard will, of course, be taken into account, but some more extreme treatments will also be applied in order to test the full potential of modern techniques.
 For more information:
For more information:
Signify
Daniele Damoiseaux, Global Marcom Manager Horticulture
[email protected]
www.philips.com/horti
