Fruit and vegetables retain a lot of heat from the field even after they are harvested. This residual heat accelerates the aging process and even causes fruit and vegetables to decompose. Furthermore, the residual heat affects the freshness and color of the product. A quick and even method of eliminating residual heat is therefore a key issue for storage and transport, regardless of the type of fruit or vegetable. This is the process referred to as 'pre-cooling'. Of course, this method is not sufficient for the preservation of freshness in fruit and vegetables. There are many different problems involved that each require a suitable solution. For example, the water content of products needs to be controlled, the damage done by machinery should be minimized, and the growth of bacteria should be limited. Arvin Lau of Vegfor Cooling Technology Limited explained four different 'pre-cooling methods in detail, with a specialized analysis of the benefits and disadvantages for the industry.
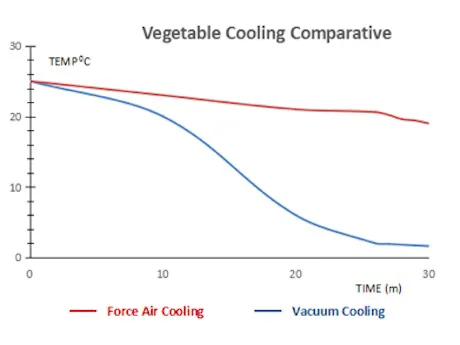
Comparative data for vegetable cooling methods
"In my experience in the fruit and vegetable industry there are four effective methods for pre-cooling fruit and vegetables: airflow cooling, forced air cooling, water cooling, and vacuum cooling. Each method has pros and cons. Only users are able to understand in detail the advantages and disadvantages of each method and make a balanced decision." This is according to Arvin Lau.
"Airflow cooling refers to a method where cold air circulates around the products to cool them. After packaging, the products can be kept in warehouses as low temperatures. There remains a space between the boxes of fruit and vegetables, and the cold air in the warehouses carries away the residual heat from the fruit and vegetables. This method is suitable for all kinds of fruits and vegetables. The advantages of this method include the following: clean and simple, the installation and maintenance cost is relatively low, and the pre-cooled products can be stored afterwards. The disadvantages include the following: the cooling process is slow and uneven. Furthermore, since the process takes a long time, this method is not suitable for leaf vegetables, which may dry out."
"Forced air cooling refers to a method where cold air is forced past the fruit and vegetables to quickly expel residual heat. The products are lined up on trays and the cold air is forced directly over the fruit and vegetables instead of circulated along the sides of the boxes. This method is sometimes referred to as cold draft pre-cooling. Advantages of this method include: clean and simple, high capacity for dispersal of residual heat, and the cost of installation and maintenance is relatively low. Disadvantages include: the method is slower than vacuum cooling and may cause some damage to the product. Furthermore, the fruit and vegetables easily dry out during this process.
"Water cooling refers to a method where fruit and vegetables are submerged in cold water. The water draws out the residual heat. This method is often used during transport. This method is suitable for products that are easily damaged by frost such as cauliflower, sweet corn, carrots, and onions. The advantages are as follows: the cooling method is relatively quick and effective, and also cleans the vegetables (for example with the use of chlorine), which helps to prevent the product from going bad. The disadvantages are as follows: this cooling method requires the additional step of drying the product afterwards. Furthermore, the water in the cooling tank needs to be monitored and regularly cleaned. The water can be harmful to some types of fruit and vegetable."
"Vacuum cooling is the quickest known method for pre-cooling fruit and vegetables. This method improves the product quality and extends the shelf-life of fruit and vegetables. Furthermore, this method lowers the overall cost of the cooling process. The advantages of this method include the following: quick and even cooling, and highly effective. This method maintains the freshness of the product. Furthermore, this method is suitable even for fruit and vegetables harvested under poor weather conditions (such as rain). Disadvantages include the following: this method is extremely suitable for leaf vegetables, mushrooms, peppers, corn, and strawberries, but not for some of the thicker, sturdier fruit and vegetables such as mangoes, carrots, and tomatoes."

Vegfor 2 carbine vacuum cooling machine
Contact person: Arvin Lau
Company name: Vegfor Cooling Technology Limited
Company address: No. 8 South Industrial Road, Songshan Lake DG, China, 52300
E-mail address: arvin.lau@vegfor.com
Company website: https://www.vegfor.com
